Ergonomic Desk Height Calculator
This free tool allows you to quickly calculate your ideal ergonomic desk height and chair height so that you can set up your office or workstation to allow for proper posture and improved health.
Simply choose your height from the drop-down box and we will provide the correct ergonomic desk height, ergonomic elbow height, and ergonomic chair height for most people that are your height.
If you'd like more specific details about how to adjust your desk, monitors, and chair to create an ideal ergonomic office set up (whether you use a traditional desk or a standing desk), we provide specific, in-depth, and medically-backed recommendations lower on this page.
If you are an HR rep or workplace wellness advocate, you'll also find a free, print-ready download that you can print out and hang in your office break room or common areas lower on this page. We've also included a free infographic which you can share on your website, blog, or intranet.
Simply choose your height from the drop-down box and we will provide the correct ergonomic desk height, ergonomic elbow height, and ergonomic chair height for most people that are your height.
If you'd like more specific details about how to adjust your desk, monitors, and chair to create an ideal ergonomic office set up (whether you use a traditional desk or a standing desk), we provide specific, in-depth, and medically-backed recommendations lower on this page.
If you are an HR rep or workplace wellness advocate, you'll also find a free, print-ready download that you can print out and hang in your office break room or common areas lower on this page. We've also included a free infographic which you can share on your website, blog, or intranet.
Calculate Your Ergonomic Desk Height and Chair Height
Please note that every individual's proportions are slightly unique, and these heights are offered as a general guide for the approximate ergonomic position for most people. This is not intended to be medical advice. We have included medically-backed research and facts below so you can tune these measurements slightly (if needed) to create your perfect ergonomic workstation and prevent injury at work.
What is Ergonomics?
The University of North Carolina defines Ergonomics as "the study of people in their working environment."
For many years workers were expected to adapt and adjust their bodies to the work they were performing, but an ergonomist is a trained professional that works to modify a person's work and working environment to fit the worker with the goal of eliminating worker discomfort and reducing the worker's risk of injury.
For many years workers were expected to adapt and adjust their bodies to the work they were performing, but an ergonomist is a trained professional that works to modify a person's work and working environment to fit the worker with the goal of eliminating worker discomfort and reducing the worker's risk of injury.
"Ergonomics (or human factors) is the scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of the interactions among human and other elements of a system, and the profession that applies theory, principles, data, and methods to design in order to optimize human well-being and overall system performance." - International Ergonomics Association Executive Council
Ergonomic Injury Statistics
According to OSHA, 33% of all worker injury and illness cases are caused by Musculoskeletal disorders which are often caused by poor workplace ergonomics. Common examples of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) include:
The USA Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that non-fatal work-related injuries occurred 2.9 million times in 2016 (the most recent year for which data is available). Discounting the productivity losses ergonomic injuries represent, these numbers represent a significant financial liability to employers in the form of tens of millions of dollars in annual worker's compensation claims. Investing in ergonomic equipment and training is in the best interest of every company.
How to Create an Ergonomic Desk Workstation
To fine-tune the ergonomic desk height calculator and chair height calculator on this page, refer to these research-backed tips from UCLA to customize your workstation for ergonomic excellence and to prevent injury.
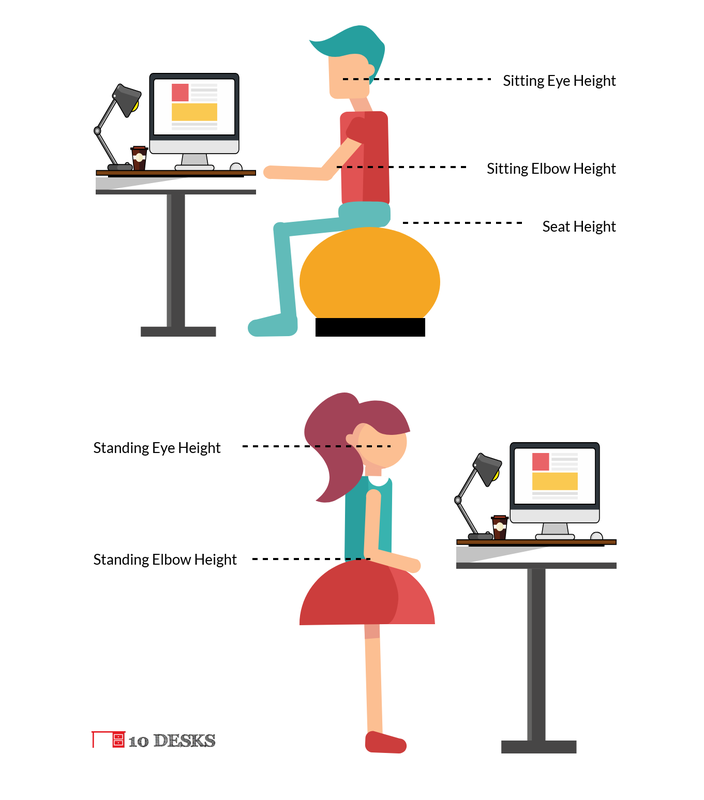
Chair ErgonomicsWhen sitting at your desk chair, make certain that your hips are positioned as far back in the chair as they can go. Adjust the height of your chair so that your feet are flat on the floor and your knees are equal to, or slightly lower than your hips. The back of your chair should be positioned in a 100-110 degree reclined angle and both your upper and lower back should be supported by the chair. Small ergonomic pillows should be used if your desk chair lacks support for your back. Adjust the armrests of your chair so that your shoulders are in a natural, relaxed position and if they are in the way, remove the armrests from your desk chair. If your ergonomic office chair allows for it, make slight changes in positioning throughout the day.
If the height of your desk or keyboard requires you to raise your chair height so that your feet dangle, use a footrest to support your feet and legs. |
Mouse & Keyboard ErgonomicsIf possible, an articulating keyboard tray should be attached to your desk and used, as it can offer you the ability to fine-tune positioning for ideal ergonomic placement. It should have room for your mouse (to keep it close), and should not interfere with your leg positioning. The primary thing to remember about ergonomic keyboard and mouse positioning is to keep everything close and avoid having to reach to use your peripherals. Position the keyboard directly in front of your body, and make sure it is close to you with the section you use most frequently centered in front of you. Keyboard height should allow your shoulders to be relaxed, your elbows in a slightly open position (100-110 degress vs. 90 degrees), and your wrists and hands should be straight and in line with the angle of your arms. A negative-angle keyboard tray can be ideal for this. Palm support in front of your keyboard may also help. Your mouse should be as close as possible to your keyboard to avoid over-reaching, and you can use a cushioned mouse pad to keep your hand and wrist properly positioned if necessary.
|
Monitor, Documents, Telephone ErgonomicsIt is important to position the top of your computer monitor 2-3" above eye level, and to keep that height consistent if you alternate between sitting and standing at a height-adjustable desk. Center the monitor directly in front of you and above your keyboard tray. You should be seated or standing at least one arm's length away from your computer screen and adjust objects on your screen appropriately to make them easy to see.
Reduce glare on your computer screen by positioning the screens at right-angles to windows if possible, and if not possible adjust curtains or blinds in your office to diffuse light and prevent glare. Vertical screen angle should be adjusted to reduce glare from overhead lights, and optical glass glare filters or secondary task lights may be used to adjust lighting in your office. If you use multiple monitors, swivel your chair and keyboard tray to face the screen you're working on to avoid neck strain. If you need to reference documents, position them close to you and alongside your monitor, using a document stand if possible. If you use a telephone keep it close to you, and if possible use a headset to avoid cradling the handset for extended periods of time. |
Desk ErgonomicsIf you sit at your desk be sure there is adequate clearance for your knees, thighs, and feet.
If your desk is too high to maintain proper ergonomic keyboard positioning, raise your chair so your arms and eyes are at the proper position and use a footrest or small stool to support your feet and legs. If the front edge of your desk has a hard or sharp edge, pad it or use a wrist support to avoid injury. You can use the ergonomic desk height calculator at the top of this page to gain a general sense for the best ergonomic desk position for your height, fine-tuning as needed to reflect the other ergonomic information provided on this page. |
The Importance of Pauses & Breaks

No matter how perfect your ergonomic workstation is, extended periods in any static posture can inhibit blood circulation and take a toll on your body. It is recommended that you take short breaks every 20-30 minutes that last a minute or two. A walk to the bathroom or water cooler is perfect for this.
Additionally, change tasks or position for a few minutes every hour and make sure you don't eat lunch at your desk ... giving yourself an opportunity to totally separate from your work environment and move is important to health and well-being.
If you work at a computer, avoid eye-strain by resting your eyes regularly. A good practice is to focus on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes (the 20-20-20 rule).
Finally, use correct posture when working and keep moving as much as possible throughout the day.
Additionally, change tasks or position for a few minutes every hour and make sure you don't eat lunch at your desk ... giving yourself an opportunity to totally separate from your work environment and move is important to health and well-being.
If you work at a computer, avoid eye-strain by resting your eyes regularly. A good practice is to focus on something 20 feet away for 20 seconds every 20 minutes (the 20-20-20 rule).
Finally, use correct posture when working and keep moving as much as possible throughout the day.
Print This Helpful Information to Share With Your Co-Workers
|
This information is available in PDF format which you are invited to print and post in your office's break-room or distribute to your co-workers in your corporate HR packet.
The PDF is 3 pages long and includes a description of the proper ergonomic position for your office chair, keyboard and mouse, monitor, phone, desk, and stresses the importance of resting your eyes and body with regular short stretch breaks. There is also a list of URLs where your co-workers can find additional reading and resources about proper ergonomics. Click the image to download your copy. |
Share This Helpful Information About Ergonomics as an Infographic
If you think the above information is helpful and you'd like to share it with others, I have created an infographic which you are welcome to republish (with credit to 10Desks.com as the source) on your website or intranet. You can copy and paste the provided code below to display this image on your website with a link back to this page as the source. You can also view the full-size infographic here.